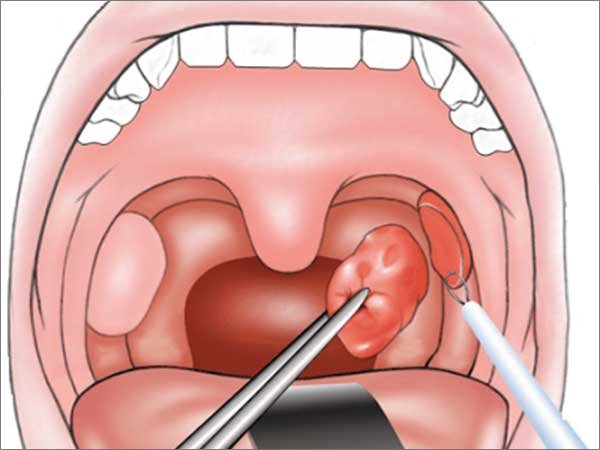
Tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure in which both palatine tonsils are fully removed from the back of the throat. The procedure is mainly performed for recurrent throat infections and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
INDICATIONS
Absolute
- Recurrent infections of throat
- ≥ 7 episodes in 1 yr
- ≥ 5 episodes/yr for 2 years
- ≥ 3 episodes/yr for 3 years
- ≥2 weeks lost school/work in 1 year
- Peritonsillar Abscess – [4-6 weeks after the abscess has been treated]
- Hypertrophy of Tonsils – [causing Airway Obstruction/ Difficulty in deglutition/ Interference in speech]
- Suspicion of Malignancy
Relative
- Diphtheria carriers
- Streptococcal carriers
- Chronic tonsilitis
- Recurrent streptococcal tonsilitis with valvular heart disease
Part of other operation
- Palatopharyngoplasty
- Glossopharyngeal neurectomy
- Removal of styloid process
CONTRAINDICATION
- Hb < 10g%
- Acute infection in URT
- Age ≤ 3 Yr
- Submucous cleft palate
- Bleeding disorders
- Uncontrolled systemic disease – Diabetes, Cardiac disease, Hypertension, Asthema
ANESTHESIA
General anesthesia with endotracheal intubation.
POSITION
Rose’s position [ Patient lies supine with head extended by placing a pillow under shoulders, A rubber ring is placed under the head ]
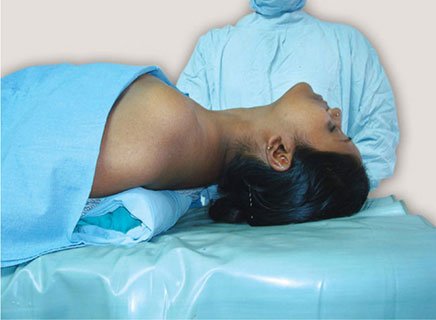
*Hyperextension of neck should be avoided.
STEPS
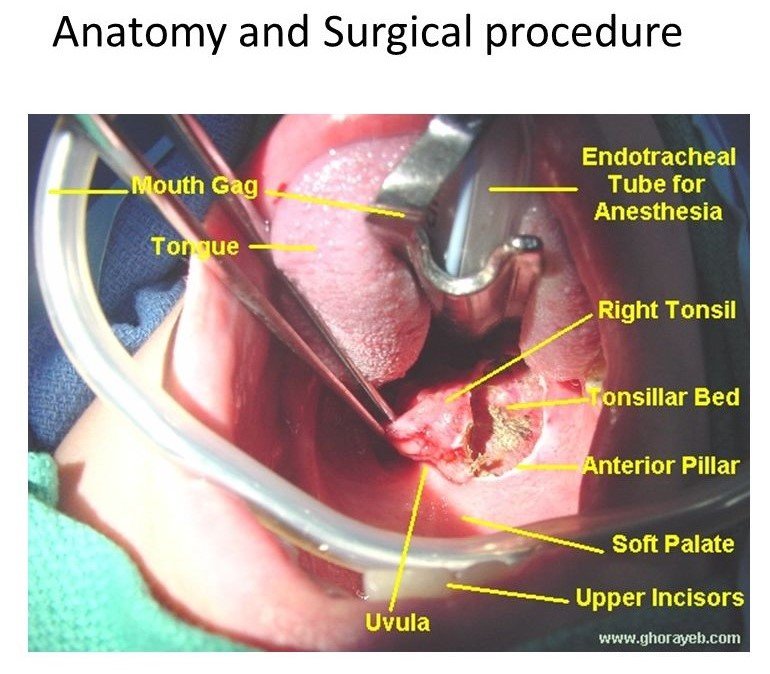
- Boyle-Davis mouth gag with Draffin’s Bipod is used to keep the mouth open.
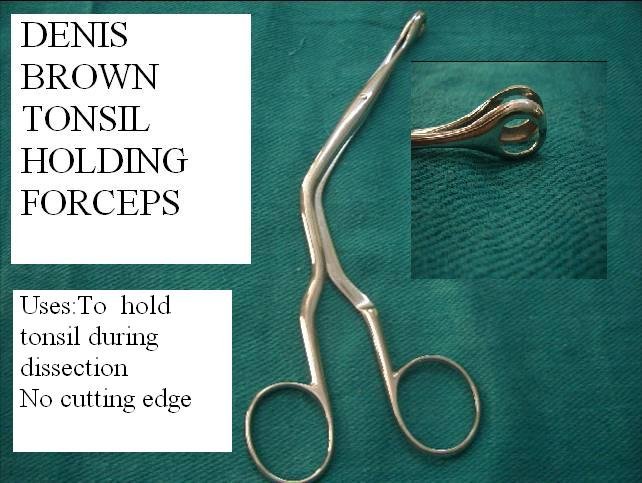
- Tonsil is held using Tonsil holding forceps and pulled medially
- Incision at mucous membrane between tonsil and anterior pillar.
- Blunt curved scissor to dissect tonsil from peritonsillar tissue to separate upper pole
- Tonsil is held at upper pole, pulled downward medially, dissection is continued till lower pole.
- Using the wire loop of Tonsillar snare the tonsillar pedicle is held, then the tonsil is cut and removed.
- Gauze sponge is applied at the fossa and pressure is applied for few minutes. Bleeding points are tied with silk
- Repeated to other side.
POST OPERATIVE CARE
- Immediate –
-
- Keep in Coma until anesthesia works.
- Keep watch on bleeding from nose/mouth
- Keep check on Vitals
- Diet – Liquid food can be taken after recovery, Ice to relieve pain, gradual build up of diet to solid food, Plenty of fluid intake.
- Oral Hygiene – Salt water gargles, Mouthwash with every feed.
- Analgesics – Paracetamol. [Aspirin/ Ibuprofen avoided due to bleeding chances]
- Antibiotics.
COMPLICATIONS
IMMEDIATE
-
- Primary Haemorrhage during operation. Controlled by pressure/ ligation/ electrocoagulation
- Reactionary Haemorrhage within 24h controlled by removal of clot, application of pressure/ vasoconstrictor
- Injury to tonsillar pillars, uvula, soft palate, teeth
- Aspiration of Blood
DELAYED
-
- Secondary Haemorrhage
- Infection
- Various lung complications
- Scarring in soft palate and pillars
- Tonsillar remnants that may be left and gets repeatedly infected.
- Hypertrophy of lingual tonsil.
INSTRUMENTS
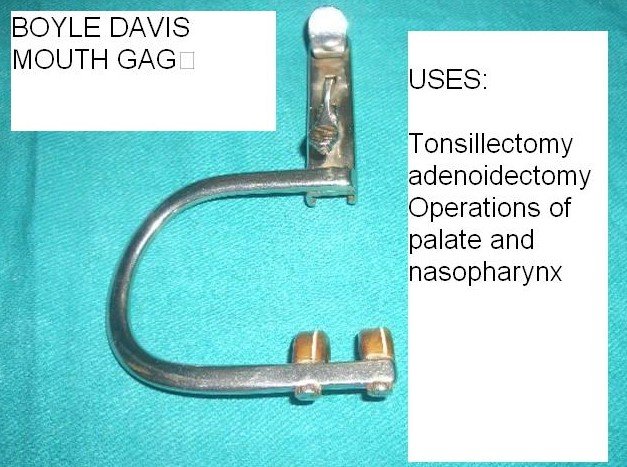
BOYLE DEVIS MOUTH GAG
DENIS BROWN FORCEPS
EVE TONSILLAR SNARE