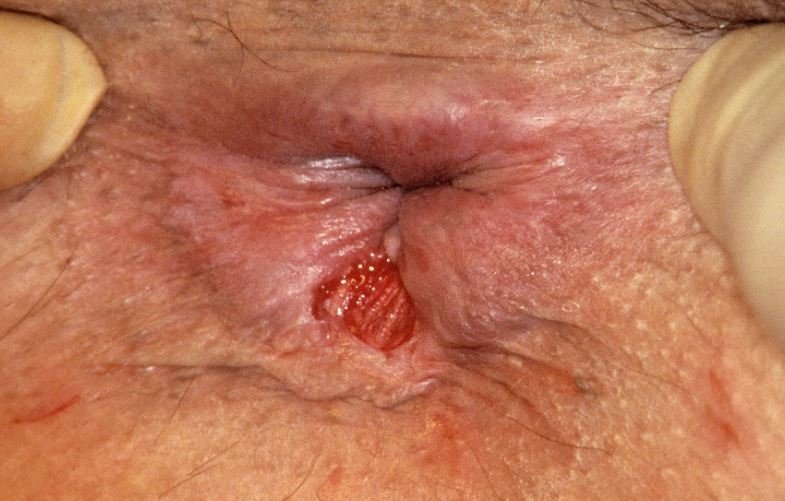
An anal fissure (also called fissure-in-ano) is a small rip or tear in the lining of the anal canal. distal to the dentate line, often due to increased anal sphincter tone.
The rule of anal fissure D’s: Distally to the Dentate line; bleeDing During Defecation; Dull puDenDal pain; Diet low in fiber
Causes
Fissures are usually caused by trauma to the inner lining of the anus from a bowel movement or other stretching of the anal canal. Constipation and passage of hard stools is often the cause of an anal fissure, although inflammatory bowel disease, anal infections, and tumors can also contribute to its development.
Pathophysiology
Overdistension or disease of the anal mucosa causes laceration or tear of the anoderm. Spasm of the exposed internal anal sphincter leads to pulling along the laceration. The anal spasm is a defense mechanism to prevent further stretching of the anal canal and worsening of the tear and causes sever pain. The posterior commissure is believed to have a very poor blood supply. And for that reason along with this anal spasm predisposes ischemia and prevents the fissure from healing. The edges of the fissures become more fibrosed, leading to a chronic fissure. The resultant pain results in voluntary avoidance of defecation and constipation, which further worsens distension of the anal mucosa. So this is a vicious cycle.
Classification
Primary (due to local trauma)
- 90% of all anal fissures located at the posterior commissure (6 o’clock in the lithotomy position)
- Chronic spasm/increased tone in the internal anal sphincter
- Low fiber intake
- Chronic constipation or diarrhea
- Anal sex
- Vaginal delivery
Secondary (due to underlying causes)
- May occur lateral or anterior to the posterior commissure
- Previous anal surgery (possible stenosis of anal canal)
- Inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s disease)
- Granulomatous disease (tuberculosis)
- Infections (chlamydia, HIV)
- Malignancy(leukemia)

Symptoms and Signs
- Sharp, severe pain during defecation. This pain typically lasts for a few hours after defecation
- Rectal bleeding (often bright red and minimal)
- Perianal pruritis
- Chronic constipation
- A small lump or skin tag on the skin near the anal fissure

Diagnosis
The diagnosis of anal fissure is often made on the basis of the patient’s medical history (See sign and symptoms and causes above).
Clinical examination
- Superficial or deep laceration in anterior, lateral, or posterior anal canal
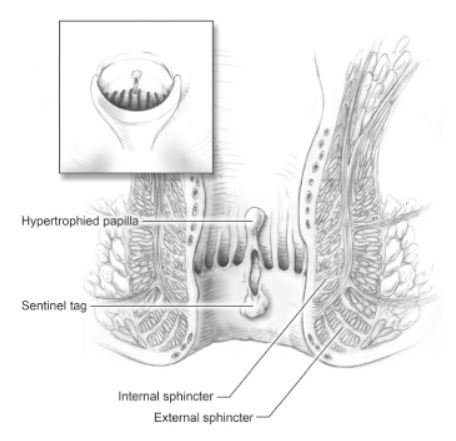
- Chronic fissures may present with fibrotic and infective changes – Wide, raised edges, Skin tags (sentinel pile) at the fissure’s distal end, Hypertrophied anal papillae at the fissure’s proximal end.
If diagnosis is unclear then Digital rectal examination is done with lidocaine 2% jelly. If the patient tolerates the digital examination, then anoscopy can be performed.
Treatment
Conservative
- First-line treatment for most anal fissures
- Dietary improvement (e.g., adequate ingestion of dietary fiber and water)
- Stool softeners (e.g., docusate)
- Anti-inflammatory and analgesic creams and/or suppositories (e.g., 2% lidocaine jelly)
- Sitz baths
- Local anesthetic injection
- Topical vasodilator therapy: calcium channel blocker gel (e.g., nifedipine) or glyceryl trinitrate ointment (GTN)
- Botulinum toxin A (BTX) injection into the internal anal sphincter. BTX induces relaxation of the hypertonic anal sphincter by inhibiting the release of acetylcholine.
Surgical
Indicated when conservative treatment is unsuccessful. The risk of fecal incontinence (e.g., high in multiparous or elderly patients) determines the type of surgical intervention.
Low risk
- Sphincterotomy (Lateral internal sphincterotomy, Posterior sphincterotomy)
- Anal dilatation (although there is a high risk of fecal incontinence with this procedure)
High risk
- Anal advancement flap
- Fissurectomy (excision of the fissure)
Differential Diagnosis
- Perianal ulcer
- Anal fistula or abscess
- Anal carcinoma