INTRODUCTION AND LOCATION
The mammary glands are paired structures that contain glandular tissue and variable amount of fat. It is actually a large sweat gland and modified apocrine gland. This modified apocrine gland extend from 2nd to 6th rib and the nipple position is present commonly at 4th intercoastal space. Horizontally it is present at lateral border of sternum to mid-axillary line.
DEVELOPEMENT
- It starts at 7th week of the fetal development.
- So, it actually starts as a thickening along the mammary rich called as milk line of schultz (Extends mainly from axilla to the groin)

Developmental anomalies:
- Amastia – absence of the breast.
- Polymastia – presence of more than 2 breasts.
- Polythelis – presence of additional nipples.
- Athelia – absence of nipples.
- Gynaecomastia – developement of breasts in a male.
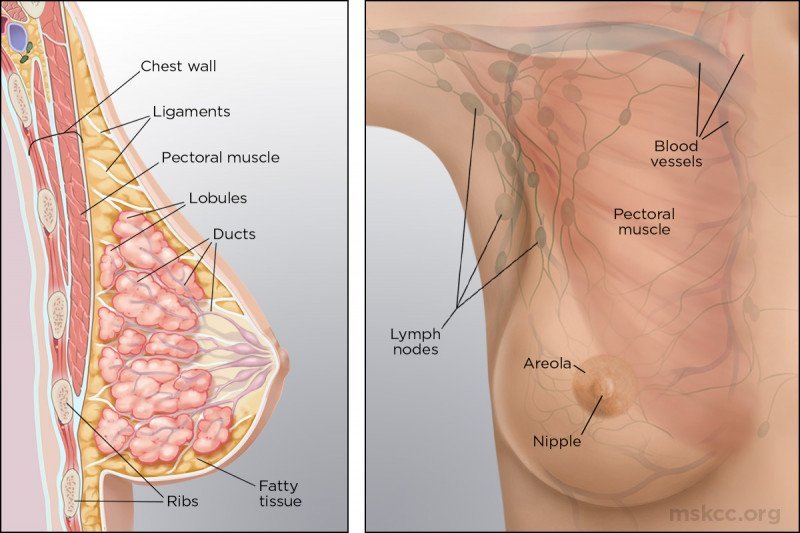
STRUCTURE OF BREAST
1. Skin:
| Nipple | Areola |
|---|---|
| Present at 4th intercoastal space | Pigmented skin around base of nipple |
| Innervated by sensory nerve ending. The nipple is most sensitive to tactile stimulation. | Contains modified sebaceous gland which prevent them from drying and cracking. |
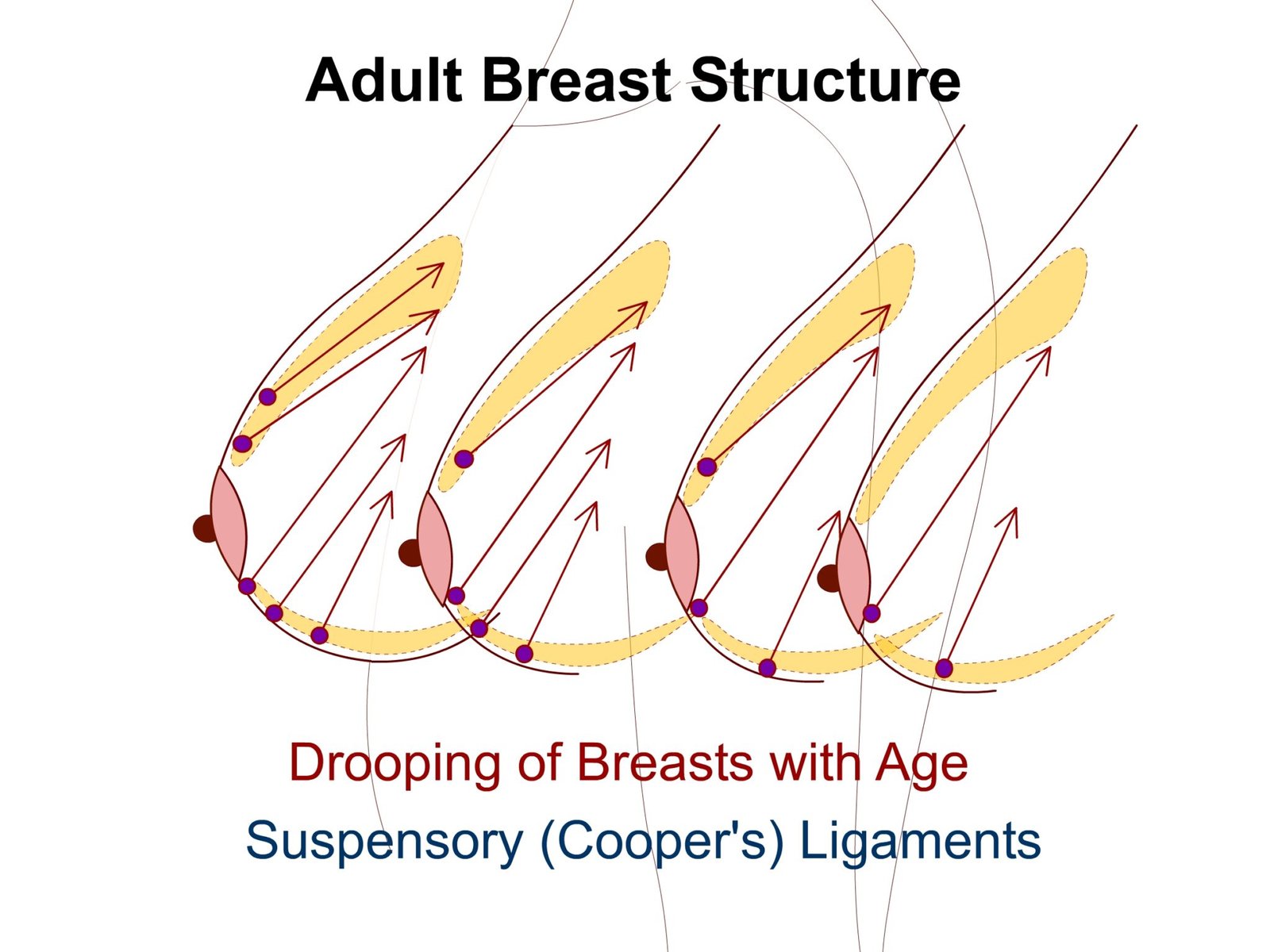
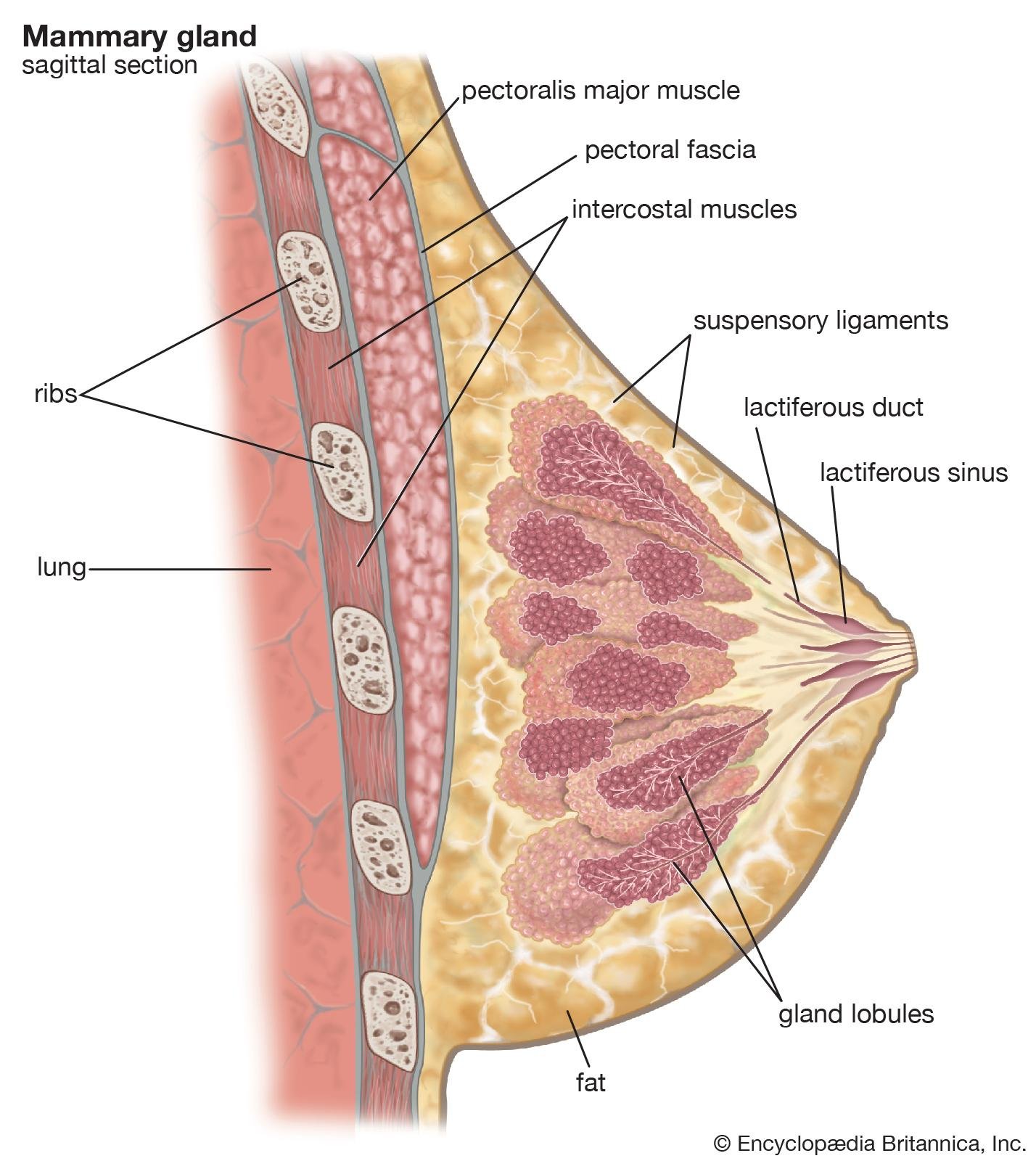
2) Stroma: Connective tissue and fat supporting framework of breast. At some point it will condense and will lead to formation of fibrous strand which are called as suspensory (cooper’s ligament). It maintains protuberance.
3) Parenchyma: It secrete milk.
4) Glands: The glandular tissue of each breast is divided into 15-20 mammary lobes containing clusters of alveoli. The alveoli open into mammary tubules. The tubules of each join to form a mammary duct. Several ducts join to form a wider ampulla, which is connected to lactiferous duct through which milk is sucked out.
BLOOD SUPPLY
| Arterial supply | Venous supply |
|---|---|
| Internal thoracic artery | Internal thoracic vein |
| Axillary artery | Axillary vein |
| Posterior intercoastal artery | Posterior intercoastal vein |
NERVE SUPPLY
Somatosensory by anterior and lateral cutaneous branches of 2-6 intercoastal nerve.

LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE
Lymphatic vessels:
- Superficial – skin of breast except nipple and areola
- Deep lymphatics – parenchyma, nipple and areola

| Upper lateral | Upper medial | Lower lateral | Lower medial | Deep |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.Anterior axillary or pectoral group of lymph nodes
2.75% lymph drains here.
|
1.Internal mammary lymph nodes
2.20% lymph drains here . |
1.Posterior intercoastal nodes
2.5% lymph drains here. |
1.Sub diaphragmatic and sub peritoneal lymph plexuses | 1.Apical group of axillary lymph nodes. |
CLINICAL ANATOMY
Breast cancer
- Arises from epithelial cells of lactiferous ducts.
- 60% cases occurs in upper lateral quadrant.
- Metastasis along lymph vessels to regional lymph nodes.
- Lower medial quadrant draining to subperitoneal lymph plexuses will further go to ovary and cause secondary ovarian tumor known as ‘krukenberg’s tumor’.





wonderful 👍 ma’am…. please do more content about anatomy topics… keep going 🤗