♥ Author Talk ♥
In this section I will try to cover the important anti fungal drugs which are used in majority of fungal infections. The most important thing about anti fungal drugs is their mechanism of action and uses of these drugs. So I will try to cover them one by one.
Different Anti-fungal drugs
Amphotericin B
MOA – There are two mechanisms of action of this drug
- Old – Forming pores on fungus
- New – Squatters Ergosterol like a sponge in cell membrane.
Route of administration – Intravenous
Uses –
- It is the Drug of choice in systemic fungal infection except invasive aspergillosis.
- It is the Drug of choice in Mucormycosis, Kala Azar, Cryptococcal meningitis.
Side effects –
- Hypokalemia – Prevented by KCL
- Hypomagnesemia
- Hypotension
- Infusion reaction -fever, chills.
- Nephrotoxicity – To prevent it, preload patient with 1-2L NACL.
Flucytosine
Flucytosine is a prodrug of 5- Flurouracial.
MOA – By inhibiting the DNA synthesis and nucleic acid synthesis
Route of administration – Intravenous
Uses – Used in cryptococcal meningitis.
Side effects –
- Bone marrow suppression
- Alopecia
- Liver dysfunction.
Azoles
Most important anti fungals are Azoles
MOA – By inhibiting the 14 alpha sterol demethylase enzyme which is responsible for conversion of lanosterol to ergosterol.
Classes –
- IMIDAZOLE – Ketoconazole, Miconazole, Clotrimazole
- TRIAZOLE – Fluconazole, Itraconazole, Posaconazole, Voriconazole
Fluconazole – It is the drug of choice in Coccoidal meningitis, Candida (C. albicans).
Ketoconazole – Use in Cushing’s disease.
Itraconazole – It is the drug of choice in Endemic Mycoses, Sporotrichosis.
Voriconazole – It is the drug of choice in treatment of Invasive Aspergillosis, but if no response occur then we can give Posaconazole.
Posaconazole – It is the drug of choice in Prophylaxis of Invasive Aspergillosis
Side effects –
Major side effect is hepatotoxicity
- Fluconazole – Alopecia
- Itraconazole – Edema
- Voriconazole – Visual abnormalities.
- Ketoconazole – Gynecomastia.
Terbinafine
MOA – By inhibiting Squalene epoxidase enzyme.
Uses –
- Maximum concentrated in Hairs, skin, nails.
- It is drug of choice in Dermatophytes.
Side effects – Hepatotoxic
Griseofulvin
MOA – By inhibiting microtubule synthesis.
Uses –
- Maximum concentrated in Stratum Corneum of skin and used in dermatophytes.
- Drug of choice in Tinea capitis.
Side effects – Hepatotoxic, Neutropenia.
Note – Fatty foods increase its absorption. So it should be given with fatty food.
Echinocandins
MOA – By inhibiting Beta glucan synthase
Uses – Used to treat Candida and Aspergillus
Topical Antifungals
We can remember these by the mnemonic BHUTAN
B – Butenafine
H – Haloprogin
U – Undecylenic acid
T – Tolnaftate
A – Azole-miconazole
N – Nystatin (used only in candida)
♥ Author Talk ♥
So these are the major antifungal drugs. I have tried to explain them in the most concise way I can and I want to summarize the whole note by a hand written diagram made by me which will help us to remember mechanism of action of these drugs.
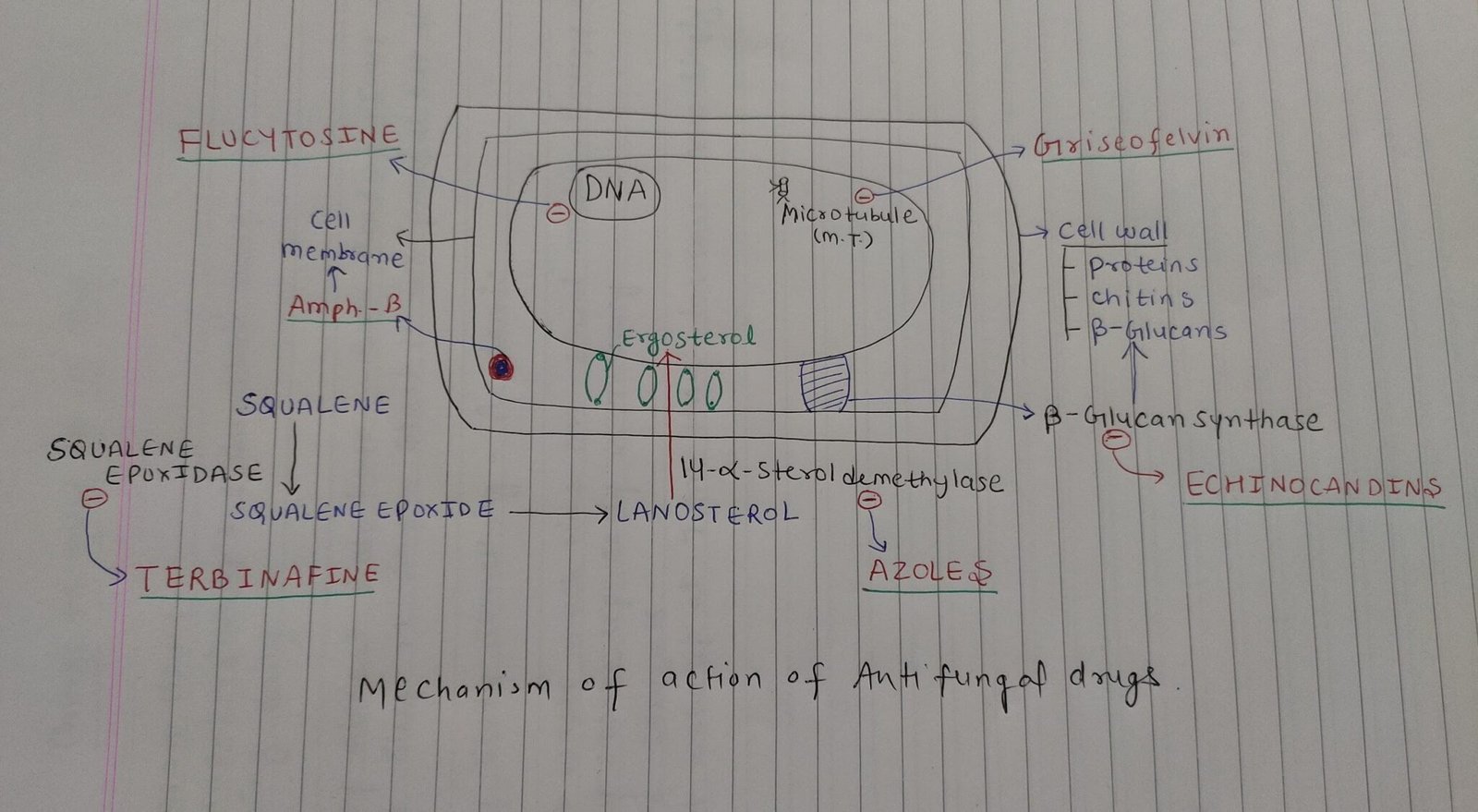
( In this diagram the words in red color are name of drugs and in black color are mechanism of action )