ROUTES OF SPREAD OF CANCER
1. Local Spread – Also called as local Invasion
2. Distant Spread – Also called as Metastasis
LOCAL INVASION
Malignant tumor spreads to its surrounding tissue by forming claw like projections. This is called as local invasion.
The tumor cells release proteolytic enzymes and damage the local basement membrane/ capsule of the organ. This process is called as invasion or infiltration.
Carcinoma in-situ –
When these are cytological features of malignancy in a tumor but microscopic examination does not show invasion of the basement membrane/ capsule. Then it is called as carcinoma in situ/ intra epithelial carcinoma/ intra epithelial neoplasm.
Example – In the uterine cervix there may be CIN (Cervical Intra epithelial Neoplasm). It is a precursor of cervical carcinoma.
DISTANT SPREAD
Hematogenous Route –
Sarcoma are usually surrounded by and rich in blood capillaries. This causes easier dissemination by hematogenous route.
Some carcinoma like those of lung, liver, kidney and prostate also spread by hematogenous route.
The direction of spread and the final site of metastasis depends on 2 factor –
1. Direction of blood flow
2. Micro environment of the tissue
This is explained by two theories –
Mechanistic theory – Determined by the pattern of blood flow.
Seed and soil theory – The provision of a fertile environment in which compatible tumor cells could grow.
Spleen is stuffed with lymphocytes, so cancer cells which reach spleen does not survive, get killed.
Some blood vessels may be devoid of valves. Through this blood vessels metastasis can occur in a direct opposite to the direction of normal blood flow.
Example – Prostatic carcinoma can spread to vertebral column by the paravertebral plexus.
Lymphatic Spread –
Carcinoma usually spread by lymphatics.
The cancer cells are surrounded by a rich network of lymphatics.
Lymphatic spread also follows mechanistic theory and seed and soil theory.
The first lymph node that is affected by metastasis in a cancer is called as Sentinel Lymph Node.
( Sentinel Lymph Node biopsy is sometimes performed intra operatively to diagnose the presence/ absence of lymphatic metastasis )
Sometimes a metastatic deposit can occlude a lymphatic channel. The metastatic cells can flow in reverse direction or this is called as retrograde lymphatic metastasis.
Transcoelomic Spread –
Sometimes cancer cells can move along the peritoneal surface. This type of spread through the body cavity is called as Transcoelomic Spread.
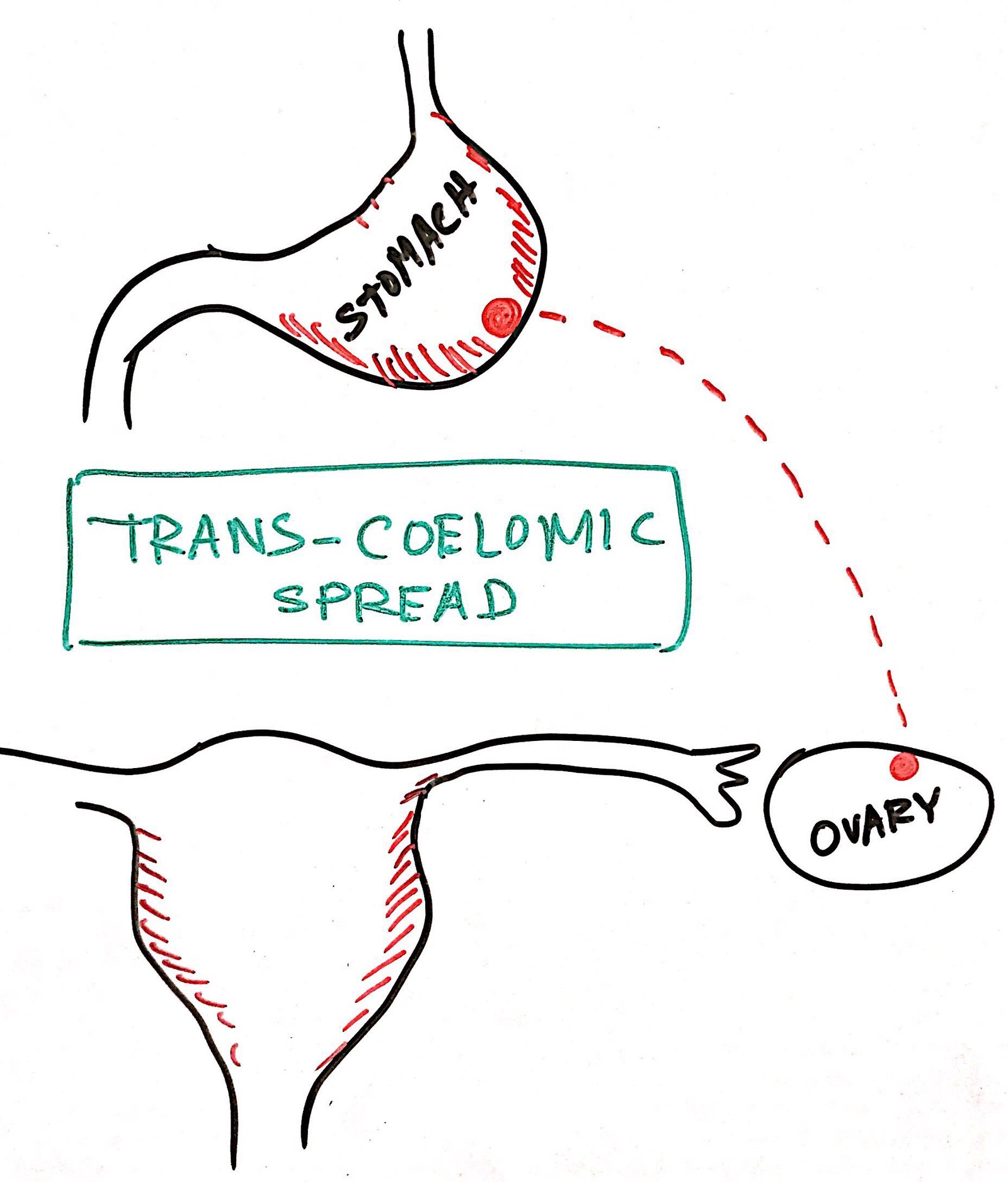
In gastric adenocarcinoma, malignant cells can spread to the ovaries forming krukenberg’s tumor.
Through Epithelial Surface –
Tumor cells from one lung can migrate along the bronchial epithelium and spread to the other lung.
This is very rare.
Direct Implantation –
During surgery cancer cells may be implanted from one sided to another by a surgical scalpel.