ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS
The Word “ANKYLOSIS” Means -Pathological fusion of bones in a joint, leading to stiffness of the joint.
It is a seronegative spondyloarthropathy, generalized chronic inflammatory disease that primarily affects the AXIAL Skeleton (Sacroiliac joint and spine) with variable involvement of root joints (shoulder and hip) and peripheral joints.
The involvement is an ENTHESIOPATHY-(Enthesis is site of attachment of tendon and ligaments to the bone ,thus enthesopathy is inflammation of enthesis).
TNF and Cytokine play central role in pathogenesis. There is autoimmunity to cartilage proteoglycan aggrecan.
CLINCAL PRESENTATION
Initial presentation is dull pain, in lower back/gluteal region.
Low back morning stiffness upto few hours ,that IMPROVES with activity .
It returns following period of inactivity.
Males are frequently affected. Age of onset b/w 15-25 years.
Most common extra articular manifestation is acute anterior uveitis.(In 30% cases).
60% develop inflammation of colon/ileum and 10% develop IBD.
Cardiac conduction defects .
Restrictive lung disease.
IgA Nephropathy.
Retroperitoneal fibrosis.

DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA
Essential criteria is Definite Radiographic sacroiliitis on MRI.
Supporting criteria: One of the three
Inflammatory back pain – Pain is classified as Pain >3 months;<40 years of age, Pain improves with exercise, Pain at night.
Limited chest expansion (<5cm at 4th Intercostal space).
Limited Lumbar spine motion (Schober test/Modified Schober test).
( >90 % of AS patients are HLA-B27 positive, whereas only 10% of normal population is HLA-B27 positive. It is not included in diagnostic criteria. )
RADIOLOGICAL FEATURES
- SI (Sacroiliac) JOINT –
Blurring of margins.
Juxta-articular sclerosis.
Erosions cause pseudo widening.
Obliteration of joint. (Ankylosis). - SPINE
Loss of lumbar lordosis=Straightening.
Enthesitis cause increased blood flow which cause Erosion of vertebral body corners, cause squaring of vertebra.
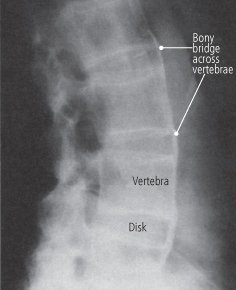
Delicate syndesmophytes, bridging vertebral bodies.
Bamboo sign,Dagger sign,Trolley track sign.
Sclerosis of margin of vertebral body- Romanus sign.
CLINICAL EXAMINATION
Tests for sacroilitis
Gaenslen test
Figure of 4 test
Pump handle test
Side to Side compression
Lumbar spine-Schober test.
Cervical spine-Fleche test.
TREATMENT
NSAIDs-Indomethacin.
Sulfasalazine and Methotrexate for peripheral joints.
Anti -TNF therapy -Infliximab/Etanercept