Introduction
- Epilepsy is the condition characterized by Recurrent episodes of seizures
- Seizures result from Episodic electrical discharges in cerebral neurons associated with prolonged depolarization during which sustained, high frequency repetitive firing occurs, followed by prolonged hyperpolarization.
- Goal of Drug is to Restore Normal Patterns of Electrical activity
Epilepsies classification
1. Generalized seizures
A. Generalized Tonic- Clonic seizures
- Major Epilepsy
- Commonest
- Last for 1-2 mins
- Unconsciousness & Tonic Spasm followed by clonic jerking & depression of all CNS function
B. Absence Seizures
- Minor Epilepsy
- Last for 1/2 min
- Momentary Loss of consciousness & patient freezes and stares in one direction.
- Little / no bilateral jerking.
C. Atonic Seizures
- Akinetic Epilepsy
- Unconsciousness with relaxation of all muscles.
D. Myoclonic Seizure
- Shock like momentary contraction of a single muscle.
E. Infantile spasms
- In infants
- Most typical epilepsy
- Muscle spasm
- Progressive Mental Deterioration
2. Partial Seizures
A. Simple Partial Seizure
- Cortical focal Epilepsy
- Lasts for 1/2 to 1 min
- No loss of consciousness
- Convulsions are confined to a particular area of cortex
B. Complex Partial Seizure
- Temporal lobe epilepsy
- Attacks of Bizarre & confused behaviors
- Emotional changes
- Purposeless movements
- Lasts for 1-2 min
- Aura (feeling & Seizures) often precedes
C. Simple Partial / Complex Partial Seizure Secondarily Generalized
- Partial Seizure occurs first and evolves into Generalized Tonic-clonic with loss of consciousness
Drug Classification
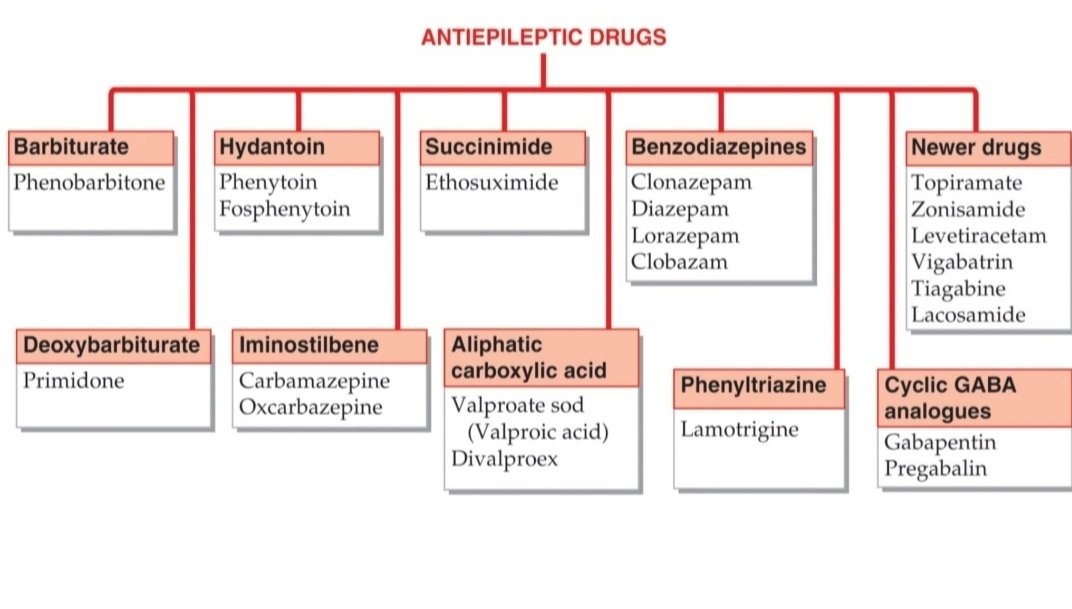
Mechanism of Action
These drugs act via various mechanisms –
- Decreased axonal conduction by preventing Na+ influx through fast Na+ channels – Carbamazepine, Phenytoin
- Increased inhibitory tone by facilitation of GABA mediated hyperpolarization- Barbiturates, BZDs
- Decreased excitatory effects of glutamic acid – Lamotrigine, Topiramate (blocks AMPA Receptors), Felbamate ( blocks NMDA Receptors)
- Decreased Presynaptic Ca2+ influx through type-T channels in thalamic neurons – Valproic acid & Ethosuximide
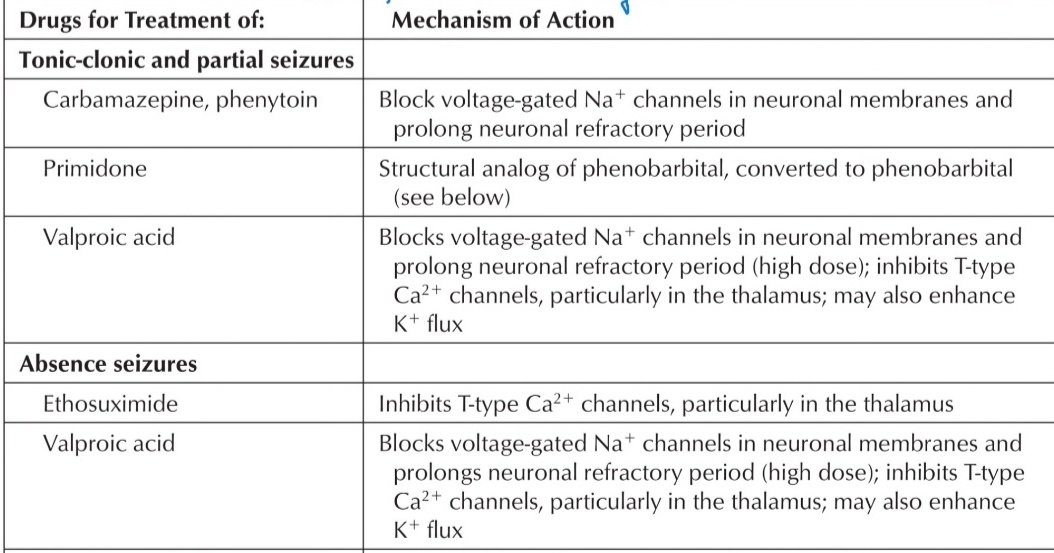

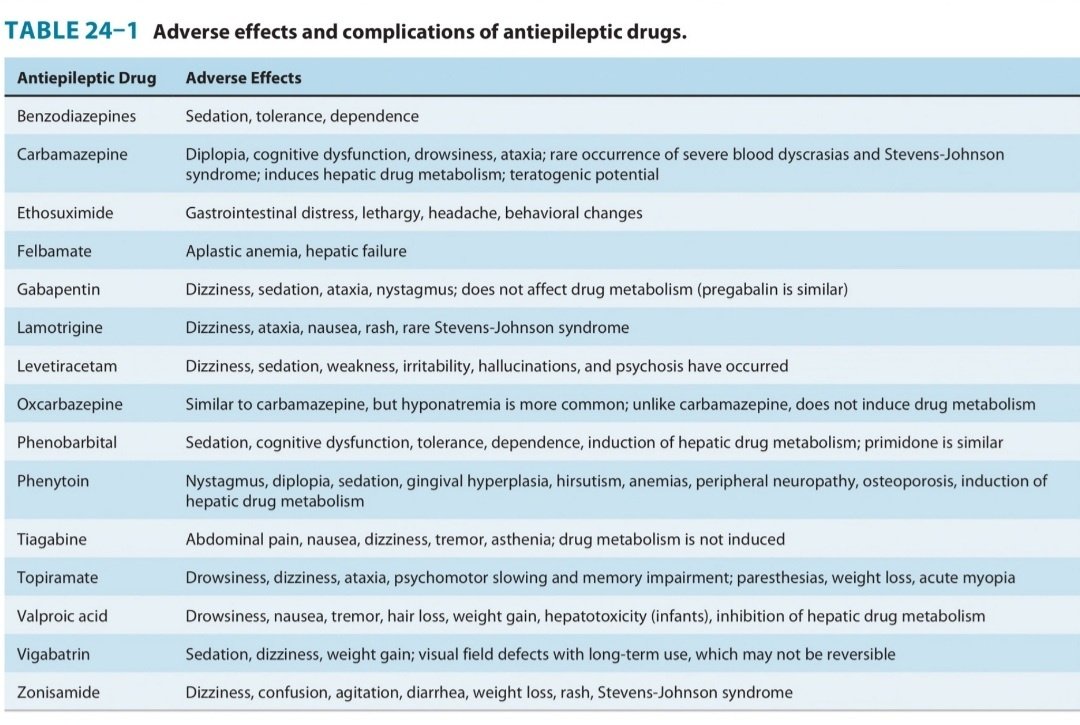
Important Antiepileptic Drugs
1. Phenytoin
Mechanism –
Blocks axonal voltage gated Na+ channels → Prevents seizure propagation
Pharmocokinetics –
- Variable absorption
- Nonlinear Kinetics
- Induction of cytochrome P450
- Zero-order Kinetics
Uses –
- GTCS
- Partial Seizures
- Status Epilepticus
- Trigeminal Neuralgia (Non Epileptic Use)
Side Effects –
- CNS Depression
- Hirsutism
- Osteomalacia
- Gingival Hyperplasia
- Megaloblastic Anemia
- Hypersensitivity/ Allergy
Contraindications –
- Myoclonic Seizure
- Absence Seizures
2. Carbamazepine
Mechanism –
Blocks axonal voltage gated Na+ channels → Prevents seizure propagation.
Uses –
- GTCS
- Partial Seizures [DOC]
- Trigeminal Neuralgia [DOC]
- Mania & Bipolar Disorder
- Diabetes Insipidus
Pharmacokinetics –
- Induces cyctochrome P450
Side effects –
- CNS Depression
- Osteomalacia
- Megaloblastic Anemia
- Aplastic Anemia
- Exfoliative Dermatitis.
- Increased ADH Secretion (Dilutional hyponatremia)
- Cleft Lip & Palate
- Spina bifida (if given to pregnant mother)
- Hepatotoxic
- Allergy (Steven Jenson’s Syndrome/ Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis)
Contraindications –
- Myoclonic seizures
- Atonic Seizure
- Absence Seizures
3. Valproic Acid
Enzyme inhibitor
Mechanism –
- Blocks axonal voltage gated Na+ channels → Prevents seizure propagation.
- But also inhibition of GABA Transaminase (increases GABA levels)
- Blockade of T-Type Ca2+ channels
- Decreases Glutamate levels
Uses –
- GTCS
- Absence Seizures
- Myoclonic Seizure
- Dravet Syndrome
- Tardin Dyskinesia
- Mania & Bipolar Disorder
- Migraine Prophylaxes
- Status Epilepticus (Used iV)
Pharmacokinetic –
Inhibits cytochrome P450
Side Effects –
(MNEMONIC – VALPROATE)
V = Vomiting, Nausea (most common)
A = Alopecia, curling of hairs
L = Liver toxicity
P = Pancreatitis
R = Rashes
O = Obesity
A = increased Ammonia
T = Teratogenic (causes Neural Tube Defects), Thrombocytopenia
E = Enzyme inhibitor
4. Ethosuximide
Mechanism –
Blockade of T-type Ca2+ channels in Thalamic neurons
Uses
- Absence Seizures
- Ethosuximide is drug of choice in children(<2yrs)
Other Ant seizure Drugs
1. Lamotrigine
- Blocks Na+ channels & Glutamate Receptors
- Also T type CCB
- Used in Various Seizures
- Side effects – Stevens – Johnson Syndrome (Rashes)
- These are safer in pregnancy [NOT TERATOGENIC]
2. Levetiractam :
- Mechanism – SV2A inhibitor
- Used in focal Onset & Generalized Tonic-clonic seizures.
- Safe in pregnancy
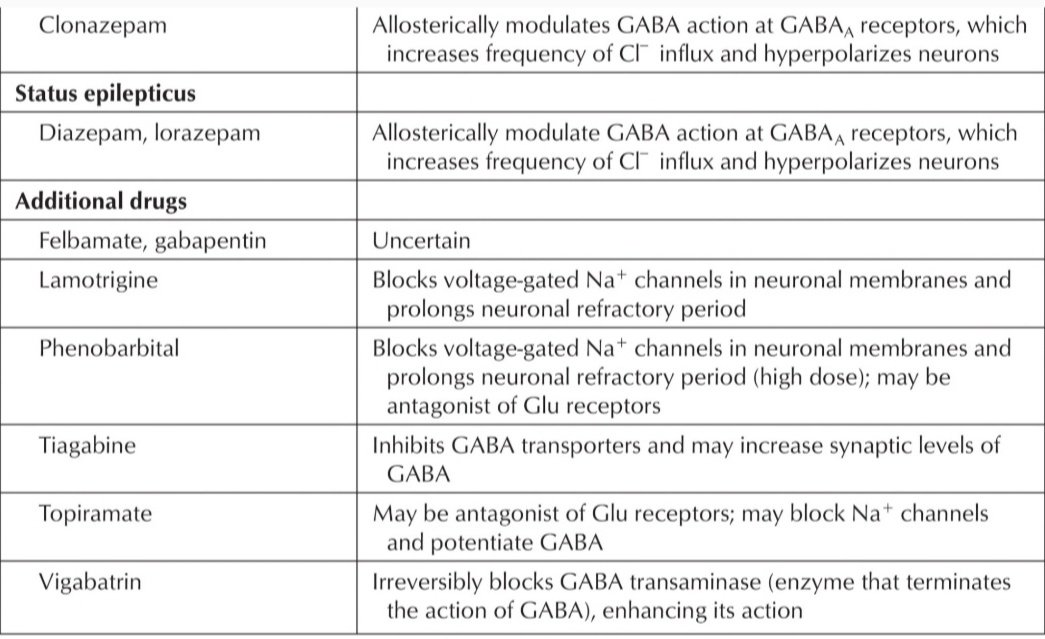
3. Topiramate
- Block Na+ channels and glutamate Receptors (AMPA blocker)
- Enhances GABA Activity.
- Also mild carbonic Anhydrase inhibitor
Uses –
- In focal seizures in adults & children > 2 years.
- Migraine prophylaxis
- Decreasing craving in Alcoholics
- Obesity
4. Felbamate
- Blocks Na+ channels and glutamate receptors (NMDA blocker)
- Used in Partial Seizure
- Side effects is Aplastic Anemia.
5. Gabapentin
- Affect Ca 2+ channels.
Uses –
- Seizure states
- Neuropathic Pain
- Post herpetic neuralgia
Side effect – Sedation
6. Zonisamfde
- Na+ channel blocker, T type Ca2+ Channel blocker
- Also Carbonic Anhydrase inhibitor
- Used in Seizure states
- Side effect is Renal Stone formation
7. Locasamide
- Na+ channel blocker
- CRMP2 Protein inhibitor
8. Vigabatrin
- Inhibits Transaminase
- Used in treatment of infantile spasms with Tuberous Sclerosis
- Side effect is leads to Visual impairment
9. Ezogabine
- K+ channel opener
- Used to treat Partial Seizure
10. Barbiturates & Benzodiazepams
They block the GABA receptor
Example –
- Clonazepam – Absence Seizures
- Lorazepam – Status Epilepticus
- Carbamazepine – Partial Seizure etc.

FINAL SUMMARY

#Know more about seizures from “THIS LINK“.
#We Partnered with Achievable.me. Check out their website for awesome study content.