♥Author Talk♥
In this section we learn about drugs acting on parasympathetic nervous system. As parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) is a division of Autonomic nervous system(ANS). So we’ll start with its comparison with its counterpart sympathetic nervous system (SNS) which is also a division of ANS.
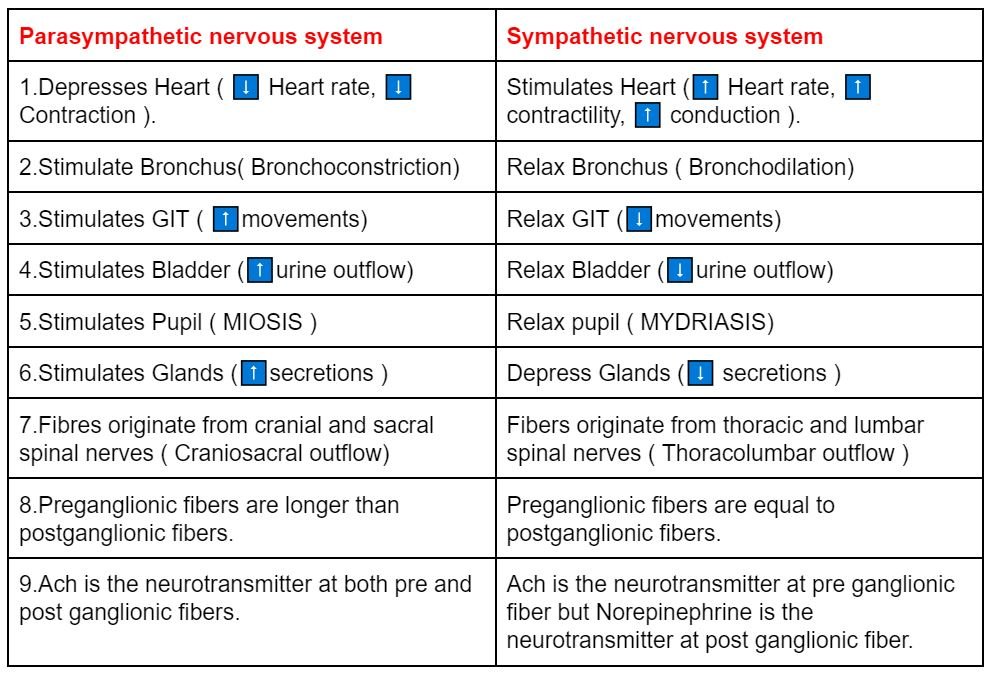
N.B – We can simply remember the difference between these two with the fact that Sympathetic nervous system will stimulate the heart and relax all the other organs and parasympathetic nervous system will depress the heart and stimulate other organs.
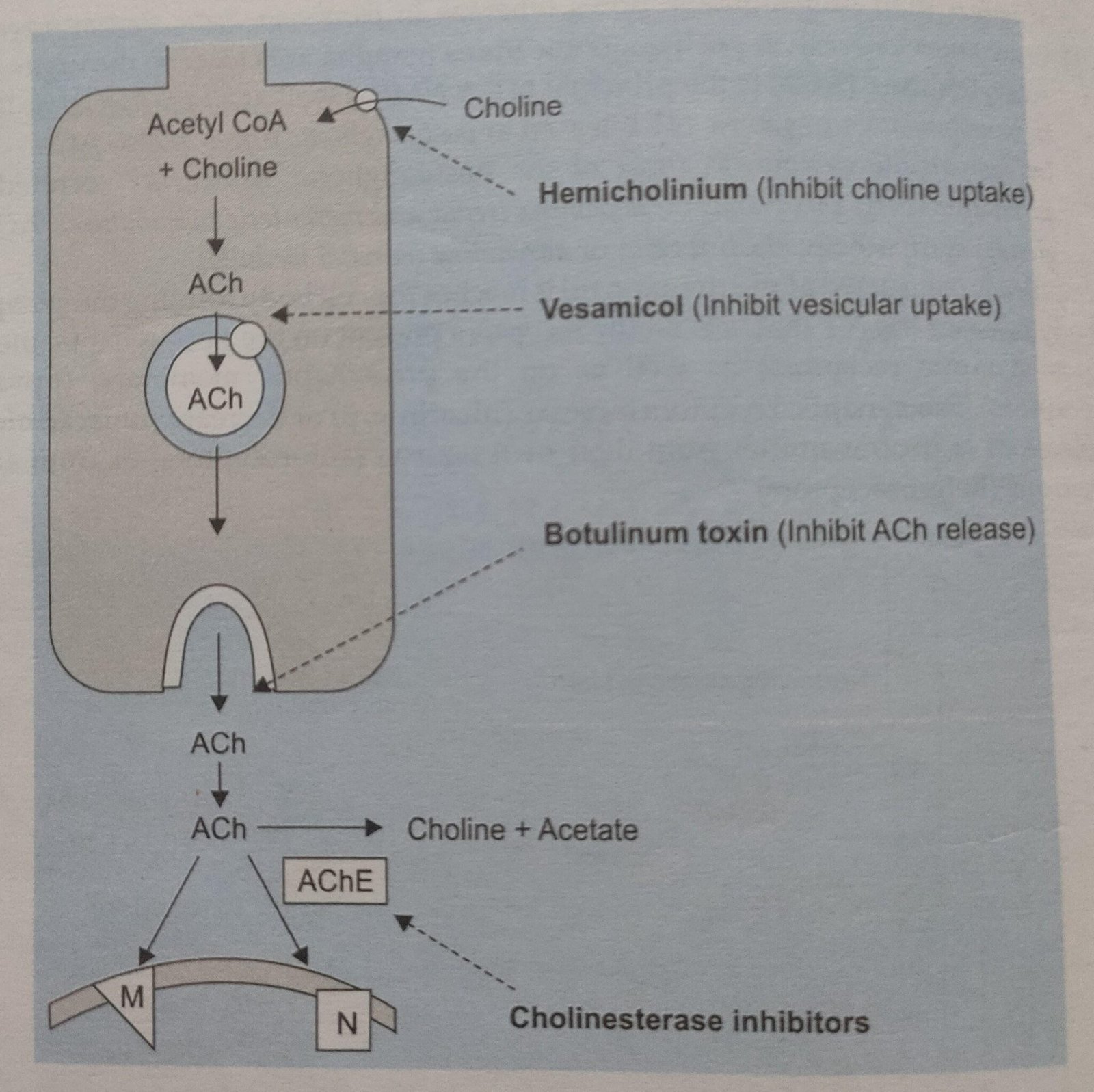
So Acetylcholine (Ach) is the principal neurotransmitter of PNS. So it is also called as cholinergic nervous system. There are some drugs which act on Ach :
- Hemicholinium – Inhibit the uptake of choline.
- Vesamicol – Inhibit vesicular uptake of Ach.
- Botulinum toxin – Inhibit the Ach release
CHOLINERGIC RECEPTORS
Two types of receptors present : Nicotinic (N) and Muscarinic (M)
Nicotinic Receptors
- Nn receptor – Act on ganglia.
- Nm receptor – Act on neuromuscular junction.
Muscarinic Receptors
- M1 – Act on stomach
- M2 – Act on Heart
- M3 – Act on eye, GIT, bladder, bronchus
- M4 – Act on CNS
- M5 – Act on CNS
MNEMONIC FOR MUSCARINIC RECEPTORS – “Phle khao pio fir dil lgao or baki kam bad mein“ I hope You can easily corelate with the mnemonic here. 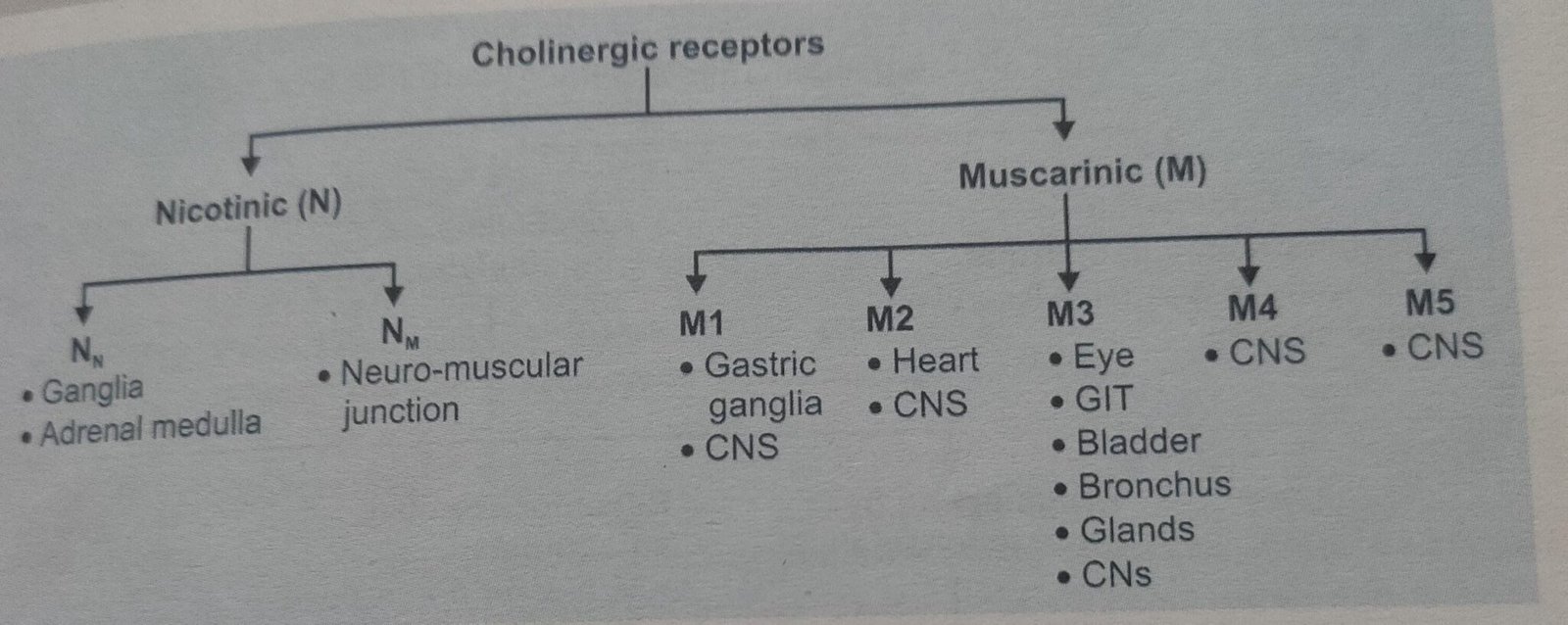
DRUGS AFFECTING PNS
Two types of drugs affect PNS which are –
- Parasympathomimetics – Cholinergic drugs.
- Parasympatholytics – Anticholinergic drugs.
Parasympathomimetics Drugs
They may act by directly activate muscarinic receptors (Directly acting) or may act by inhibiting AchEsterase enzyme so act by ⬆️ availability of Ach at synaptic cleft (Indirectly acting).
Directly acting Drugs –
Mechanism of action – Directly activate the muscarinic receptors of Ach.
PILOCARPINE – Act on Pupil by causing Miosis ( constriction of pupil) and used in Angle closure glaucoma.
BETHANECHOL – Act on Bladder by increasing urine outflow and used in Atonic Bladder.
METHACHOLINE – Act on myocardium by decreasing activity of heart and used in Tachycardia arrhythmias.
CARBACHOL – Common activity on both nicotinic and muscarinic receptors.
CEVIMELINE – Used in Xerostomia ( dry mouth) in Sjogren syndrome.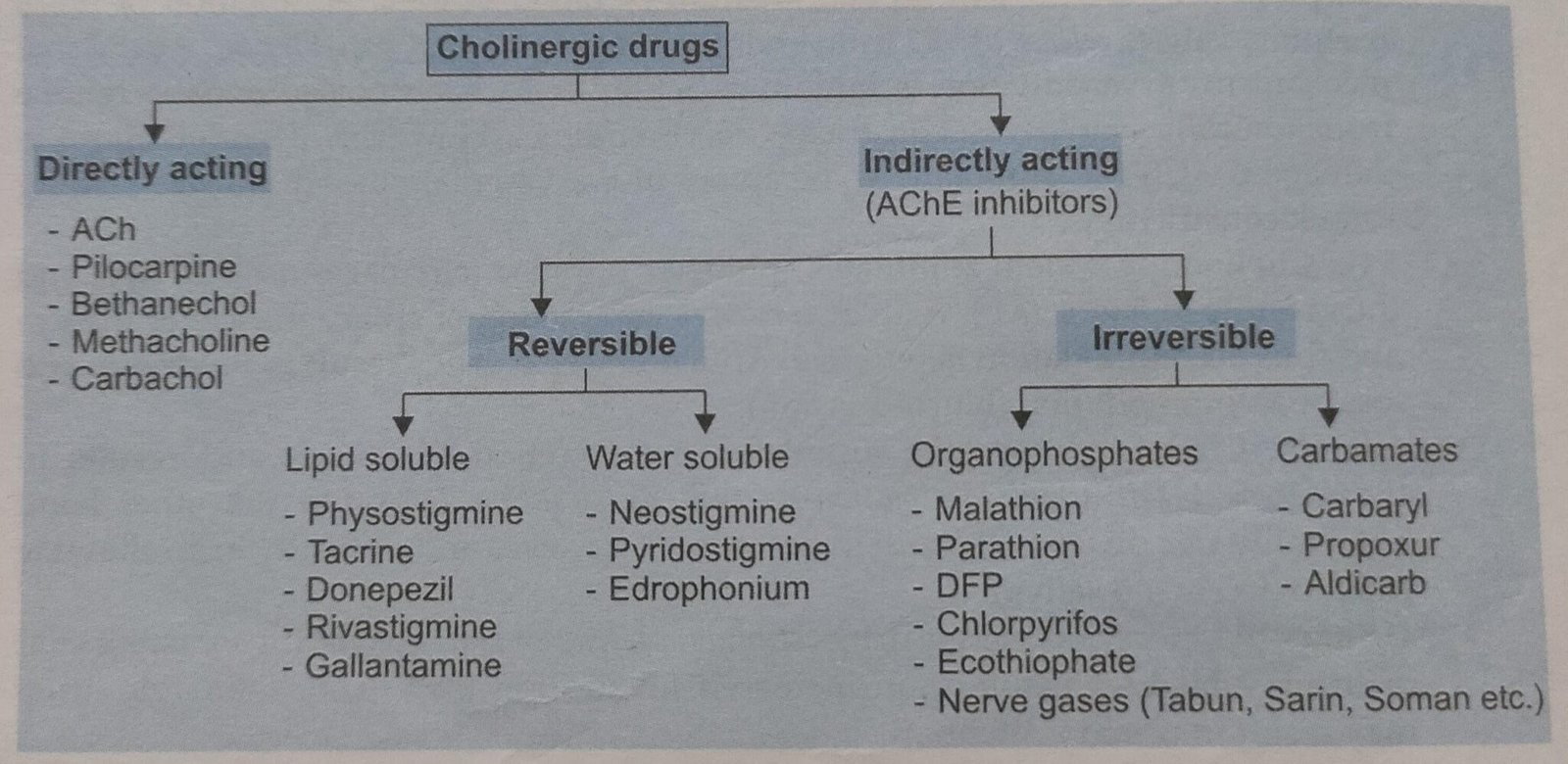
Indirectly Acting Drugs –
Mechanism of action – Act by inhibiting the enzyme acetylcholinesterase thus increasing the availability and prolonging action of Ach. Also known as ANTICHOLINESTERASES.
They may be A) Reversible and B) Irreversible
A) REVERSIBLE DRUGS
Physostigmine, Neostigmine, Pyridostigmine, Edrophonium are the important drugs in this group.
- PHYSOSTIGMINE –
- Naturally occurring tertiary amine.
- Lipid soluble – Due to its lipid solubility it can be administered orally. It can cross Blood brain barrier and pupil so it can be used in Angle closure glaucoma. It is the Drug of choice for Atropine poisoning.
- NEOSTIGMINE –
- Synthetic and quaternary amine.
- Water soluble – Due to its water solubility it can’t be given orally. It can’t cross Blood brain barrier. So they will be used when we need to produce action outside the brain.
- They don’t have any side effect on brain as they can’t reach brain.
- It can be used for the treatment of Myasthenia gravis.
- It can also be used for treatment of cobra bite, post operative paralytic ileus, post operative urinary retention.
- PYRIDOSTIGMINE-
- It is longer acting than neostigmine and can be used for myasthenia gravis.
- EDROPHONIUM –
- It is a short acting drug (<10 min ).
- Route of administration – IV
- Useful for the diagnosis of Myasthenia gravis using Tensilon Test
B) IRREVERSIBLE DRUGS
This group includes Organophosphates (Malathion, Parathion) & Carbamates (Carbaryl, Propoxur)
Symptoms – Symptoms of Anticholinesterase poisoning / Organophosphate poisoning are like cholinergic / parasympathetic symptoms which include –
- Pin point pupil (pupil constriction)
- Salivation, lacrimation, sweating, bronchoconstriction, diarrhoea, urination, bradycardia (depressive action on heart).
N.B
- Atropine is the drug of choice for organophosphate poisoning. And given IV.
- Sometimes in organophosphate poisoning Heart rate may be elevated and the reason behind it is the Ach also contains Nm receptors which can elevate Heart rate and Blood pressure sometimes.
- The most important symptoms of organophosphate poisoning are pin point pupil (pupil constriction) and increase in secretions. And atropine will be given for organophosphate poisoning every 5 minutes till the sign of atropinization reached.
Sign of atropinization
- Pupil dilation (mydriasis).
- Decrease in secretions.
Ach-Esterase Reactivators
- OXIMES – Pralidoxime, Diacetyl monoxime.
- Oximes are used only for organophosphate poisoning and not for carbamate poisoning.