Light reflex pathway
- Parasympathetic pathway
- Location – Midbrain at the level of superior colliculus
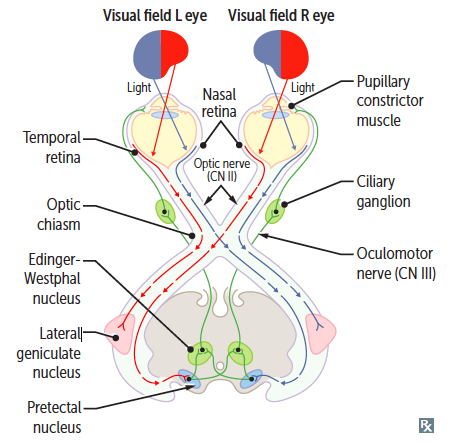
Pathway
- Optic Nerve
- Optic Chiasma
- Optic Tract
- Visual Pathway – Optic Tract to LGB to Optic Radiation
- Pupillomotor Fibers leaves the optic tract before it relays into LGB. The fibers then go to Pretectal Nuclei (Center for light reflex)
- Pretectal Nuclei (Center for light reflex)
- Interneurons/ Internuncial neuron – One half curve around periaqueductal gray and go to ipsilateral Edinger Westphal Nucleus (EWN). The other half go through posterior commissure to contralateral EWN
- Edinger Westphal Nucleus (EWN)
- 3rd Cranial Nerve (Oculomotor nerve)
- Ciliary Ganglion
- Short Ciliary Nerve
- Sphincter Pupillae
Defects
- Afferent Fibers – Optic Nerve II CN – Sensory
- Efferent Fibers – Oculomotor nerve III CN – Motor
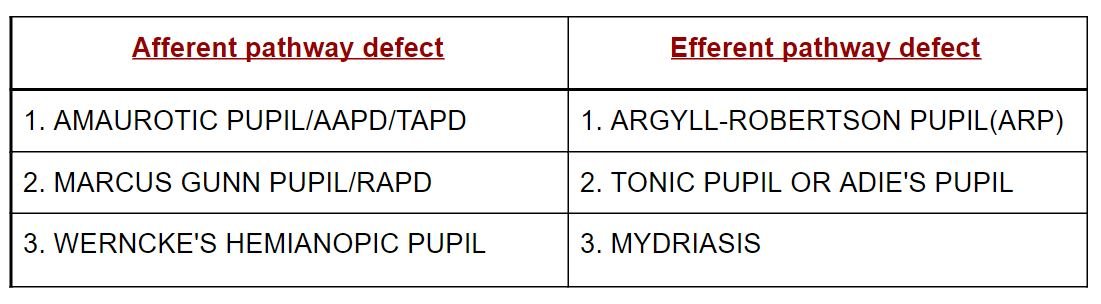
AAPD – ABSOLUTE AFFERENT PATHWAY DEFECTS
TAPD – TOTAL AFFERENT PATHWAY DEFECTS
RAPD – RELATIVE AFFERENT PATHWAY DFECT
Amaurotic pupil/TAPD/AAPD
- Site – Indicates lesion of Optic nerve / Retina on the affected side
- Absence of Direct light reflex ( DLR) on affected side
- Absence of Consensual light reflex (CLR) on other eye
- In diffuse light both pupils are of equal size
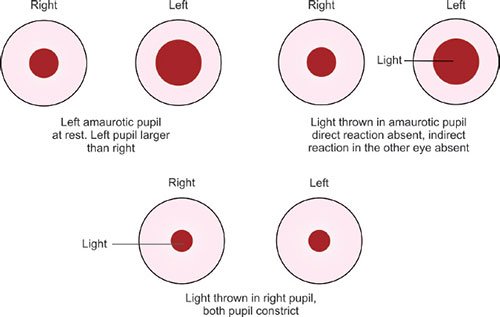
Features
- Ipsilateral Anopia( blindness) + (-) DLR + (-) CLR
- Near Reflex is present due to normal eye (Consensual)
- Isocoria (Same size of pupil)
Marcus Gunn pupil/RAPD
- Site – Occurs due to partial optic nerve lesion
- Incomplete Optic nerve lesion/ Severe retinal diseases
- Causes –
- Optic neuritis
- Retinal detachment
- Central retinal artery/vein occlusion/CRAO/CRVO
- Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (AION)
- Primary open angle glaucoma
- It is the earliest sign of optic nerve disease, even in the presence of normal visual acuity in the affected side.
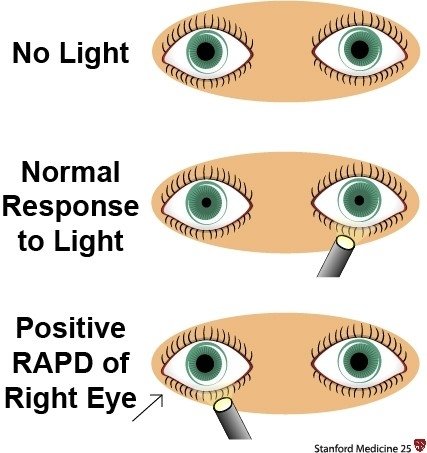
[1. On presentation both pupils are contracted (Isocoria). 2. Light on the left eye in dark room 3. Light on the right eye in dark room (RAPD Eye)]
Swinging Flashlight Test
- This is a flashlight test for RAPD
- Leads to earlier fatigue of the partially lesioned optic nerve (Right eye).
- So, on drawing light from the normal side (left), for a brief moment as both pupil are in the dark, they start to dilate.
- On reaching the right lesioned side, due to fatigue, impulse for constriction is weaker than impulse of already occurring dilation.
- So, both pupils are seen to Dilated
- This phenomenon is known as “Paradoxical dilation/ Pupillary escape phenomenon“
Wernicke’s Hemianopic pupil
- Site – Proximal optic tract
- Causes –
- Tubercular meningitis
- Syphilitic meningitis
- Cerebral artery Aneurysm
Example
(In case of Right optic tract lesion)
- If Light thrown to the temporal half of the retina of the affected side (side of visual loss) and nasal half of the retina of opposite side eye, then I/L Direct and C/L Consensual light reflex will be absent
- If Light thrown to the nasal half of the retina of the affected side (where the vision is present) and temporal half of the retina of opposite side eye, then I/L Direct and C/L Consensual light reflex will be present
- Visual field defect – Left hemianopia

Argyll Robertson Pupil (ARP)
- Site – Rostral midbrain (Aqueductal grey matter/sylvius) or Posterior commissure
- Cause –
- Neurosyphilis (tertiary syphilis)(tectum lesion)
- Tabes dorsalis
- Aortic regurgitation
- Patient’s Complain – Unprotected intercourse way back + Neurological symptoms ⇒ Neuro syphilis.
- It is bilateral presentation
- Pupil do not react to light
- Near reflex is present
Mnemonic: ARP PRA
- ACCOMMODATION REFLEX PRESENT
- PUPILLARY LIGHT REFLEX ABSENT
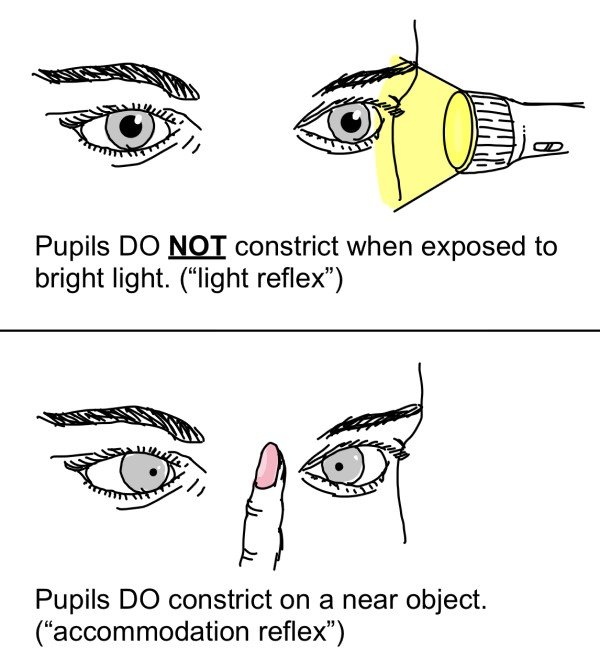
Important Points
- Pupils do not constrict with pilocarpine and dilate poorly with atropine.
- Pupils are always seen constricted, as lesion in the Rostral midbrain also damages the supranuclear inhibitory fibers to EWN. EWN keeps on releasing , parasympathetic impulse to sphincter pupillae. Thus, pupils remain constricted, and do not dilate in dark.
- No dilation lag is seen in ARP (Horner syndrome).
Tonic Pupil/ Adie’s Pupil
- Site – Parasympathetic pupillomotor damage (post ganglionic), Ciliary ganglion, Short ciliary nerve
- Causes –
- Orbital trauma
- Herpes zoster virus ganglionic (Herpes virus dormant in ganglion)
- Diabetes (Pan peripheral autonomic neuropathy)
- Alcoholism
HOLMES ADIE’S PUPIL
- Tonic pupil + Diminished deep tendon reflex
- Absent knee jerk
- Absent light reflex and slow near reflex
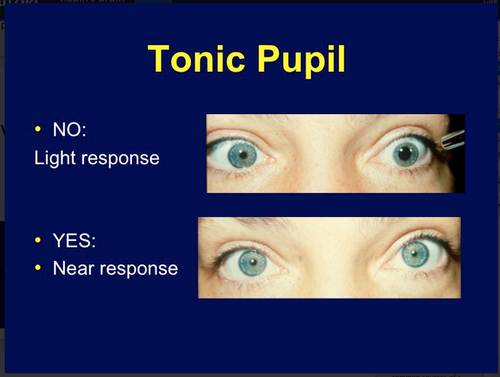
Important Points
- Near reflex is present
- Absent light reflex or show “vermiform movement contraction“
- Anisocoria – Affected pupil is larger
- Pupil constricts with 0.125% pilocarpine (Cholinergic super sensitivity)
Example
(If lesion in Right Ciliary ganglion)
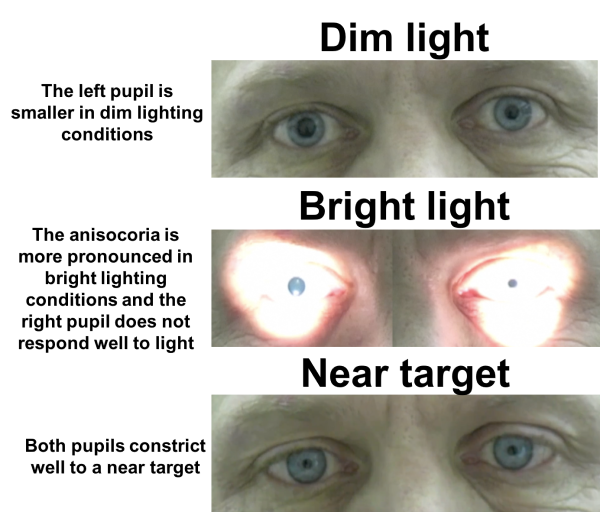
On Presentation
- Right I/L pupil – Dilated
- Left C/L pupil – Constricted
- Anisocoria
Light on Left eye
- Right C/L pupil – Do not Constricts. Consensual absent
- Left I/L – Constricts
Light on Right eye
- Right I/L pupil – Do not constricts. DLR absent
- Left C/L – Constricts. Consensual present.





Best notes thank u
Thank you for the encouraging words.
thank you