NEONATAL JAUNDICE
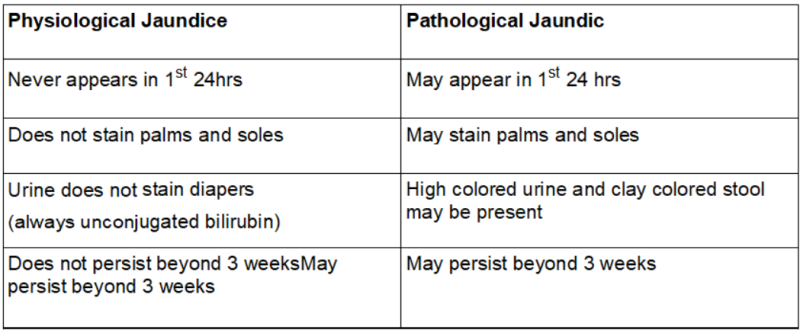
Clinical jaundice in newborn appears at bilirubin level >5mg/dl
Jaundice during 1st week of life is seen in 60% term infants and 80% preterm.
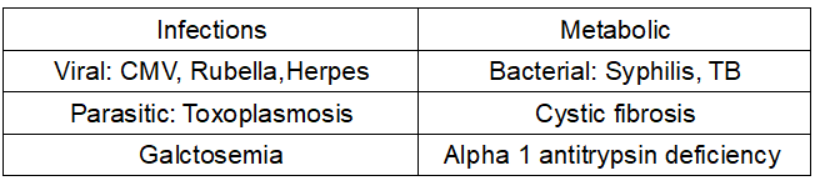
Causes of Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia
Non obstructive causes :
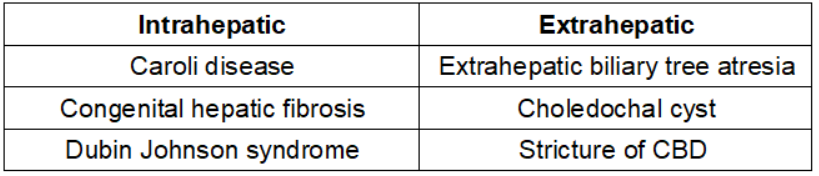
Obstructive causes :
Modified Krammer’s Rule
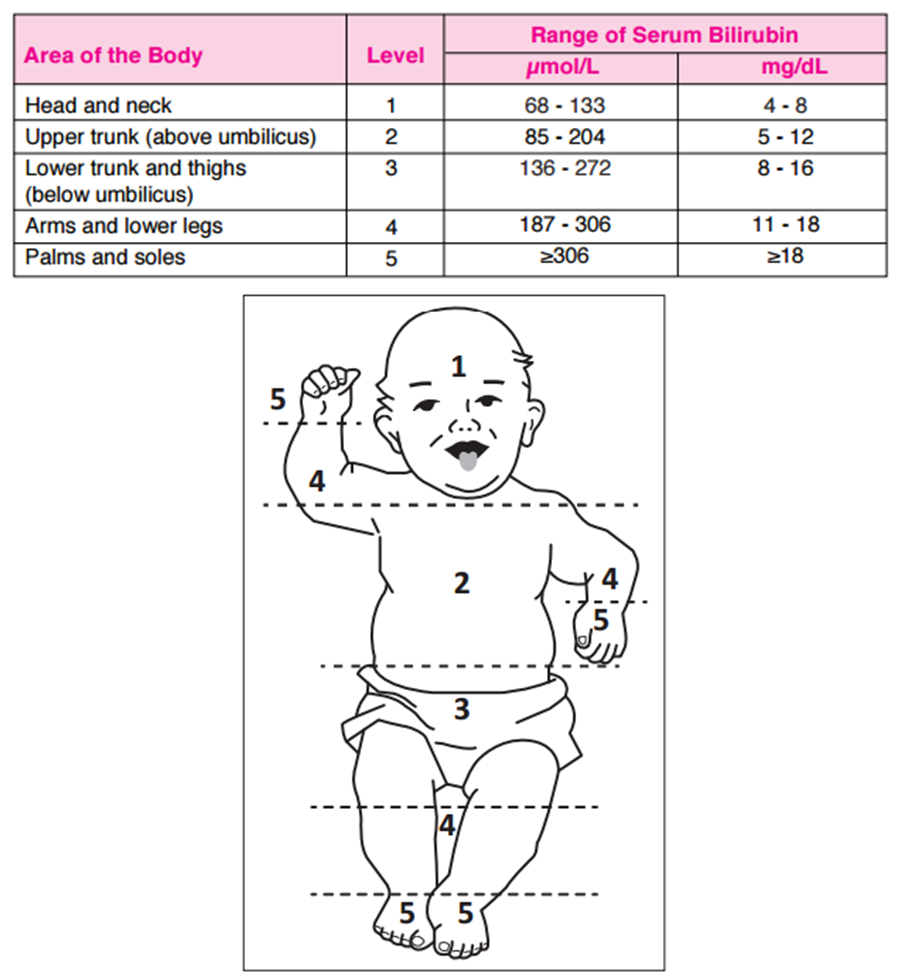
Clinical Features
Kernicterus or bilirubin encephalopathy is a neurologic syndrome resulting from deposition of unconjugated bilirubin.
Lethargy, poor feeding and loss of Moro reflex, tendon reflexes.
Opisthotonus with a bulging fontanel and shrill high pitched cry.
In advanced cases, convulsions, coma and death.
Diagnostic evaluation
- Determination of direct and indirect bilirubin
- Hemoglobin with reticulocyte count and peripheral smear
- Blood grouping and coomb’s test
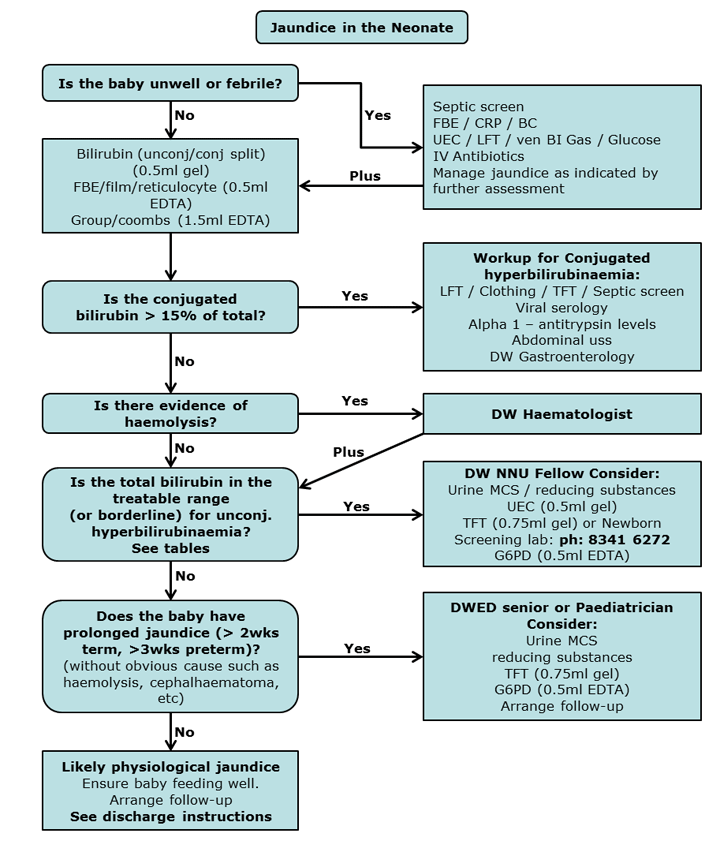
Treatment
Goal of therapy is to prevent neurotoxicity
- Phototherapy
- Exchange transfusion
- Drugs
- Phototherapy
- Most effective wavelength: 450-460nm
- Mechanisms
- Photo isomerization
- Structural isomerization: Bilirubin is converted to lumirubin which is irreversible structural isomer excreted by kidneys
- Photo oxidation
- Therapeutic effects of phototherapy depend on
- Types of lamps: LED lamps are better
- Distance between light and infant
- Surface area of exposed skin
- Complications
- Loose stools, dehydration due to increased insensible water loss
- Hypocalcemia
- Bronze baby syndrome: due to elevated conjugated bilirubin
- Retinal toxicity
- Gonadal toxicity
- Temperature disturbances
Phototherapy is contraindicated in porphyria
- Exchange transfusion
- Double volume exchange transfusion is done if high bilirubin levels and intensive phototherapy has failed
- Drugs
- Intravenous immunoglobulin
Used as adjunctive in hyperbilirubinemia due to hemolytic disease
Reduces the need for exchange transfusion by reducing hemolysis
Important points to remember
- Area of brain most commonly involved: Basal ganglia
- Extrapyramidal type of cerebral palsy seen in neonatal jaundice
- Most important mechanism of phototherapy: structural isomerization
- Effectiveness of phototherapy does not depend on pigmentation of body
- Genitalia and eyes of baby must be covered during phototherapy